To keep an eye on a webpage for changes, you set up an automated tool that regularly checks the site's content or visual layout. When it spots a difference, it shoots you an alert. This whole process takes you from manually refreshing a page to getting real-time intelligence on everything from a competitor’s new pricing to critical updates on a policy page. The most dependable methods work by comparing snapshots of a page's code or visual appearance over time.
Why Automated Webpage Monitoring Is Essential
![]()
In a world where web content is always in motion, relying on manual checks isn't just slow—it's a massive business risk. Tiny, unnoticed changes can snowball into major consequences, like missing out on a competitive edge or even falling out of compliance. Switching to an automated system turns this reactive chore into a proactive strategy, giving you a serious advantage.
Real-World Scenarios and Use Cases
Picture this: you're trying to track a competitor's pricing during a huge Black Friday sale. The manual way involves hitting refresh on their page over and over, hoping you catch the price drop. An automated system, on the other hand, pings you the second the price changes, so you can adjust your own strategy right away.
This same idea applies across so many different business functions. From marketing to legal, knowing when something changes online is often the key to making the right move.
Let's look at a few common situations where this kind of automation is a game-changer.
Key Use Cases for Webpage Change Monitoring
The table below breaks down some of the most common reasons businesses set up automated webpage monitoring. It shows how this simple technology can be applied to solve complex problems across different departments.
| Use Case | Primary Goal | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Competitive Analysis | Stay ahead of the competition by tracking their online strategy. | A marketing team monitors a rival's homepage to get instant alerts on new promotions, product launches, or messaging changes. |
| Brand Protection | Ensure website integrity and prevent unauthorized modifications. | An IT team gets an alert if their company's "About Us" page is defaced or if critical legal disclaimers are removed. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhere to legal and industry standards by tracking policy changes. | A financial services company monitors a government regulatory site to be notified of any new compliance guidelines. |
| Operational Awareness | Track changes to critical third-party dependencies. | A development team watches a partner's API documentation page to know immediately when endpoints are updated, added, or deprecated. |
As you can see, the applications are incredibly diverse, but they all boil down to one thing: turning publicly available web data into actionable business intelligence.
Relying on manual checks is like trying to catch raindrops in a storm—you'll miss most of what's happening. Automation provides the net that catches every important change, ensuring you never miss a critical update that impacts your business.
The Growing Need For Automation
Let's be realistic—the sheer scale of the modern web makes manual oversight completely impossible. This reality has fueled major growth in the website monitoring tools market, now a sector valued in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
With over a billion sites out there and roughly 175 new ones launching every minute, the digital surface area businesses have to worry about is expanding at a dizzying rate. This explosion of content makes automated tools a flat-out necessity for managing risk and staying competitive. If you're curious about the numbers, you can find more market insights on the growth of website monitoring tools.
Ultimately, learning how to monitor a webpage for changes is about building yourself an early warning system. It replaces guesswork with hard data, giving you the timely information you need to make smart decisions, protect your assets, and jump on opportunities the moment they appear.
Choosing Your Change Detection Strategy
Before you can monitor a webpage for changes, you have to answer a deceptively simple question: what is a "change"? Is it a single word? A price update? A button moving a few pixels to the left? How you answer that question determines your entire technical approach.
Picking the wrong method is a classic mistake. You'll either drown in false alarms from trivial updates or, even worse, completely miss the critical changes you were trying to catch in the first place. The real trick is to align your detection strategy with your specific goal.
The Brute-Force Checksum Method
The most straightforward way to spot a difference is with a checksum. You grab the page's entire HTML source, run it through an algorithm like MD5 or SHA-256, and get a unique hash—a short string of characters. If anything at all changes in that source code, even a single space, the hash will be completely different.
This approach is lightning-fast and requires very little processing power. The massive downside, however, is the complete lack of context. A checksum tells you that something changed, but it gives you zero information about what or where it was. A silent update to an invisible tracking script triggers the same alert as a 50% price drop.
My Take: Checksums are great for simple "yes/no" checks, like confirming a file hasn't been corrupted. For the nuance of webpage monitoring, they usually generate far more noise than useful signal.
Surgical Precision with DOM Diffing
If you need more granular control, DOM (Document Object Model) diffing is a much better tool for the job. Instead of hashing the whole page, this technique compares the structured HTML element tree from one check to the next. You can see exactly which elements were added, removed, or changed.
This is where things get powerful. You can tell your system to only watch for changes inside the <div id="price-container"> element and ignore everything else. This is how you eliminate false alarms from shifting ads or updated copyright dates in the footer. The trade-off? Implementing a reliable DOM diffing system is more complex and demands a solid HTML parser.
Capturing What Code Misses with Visual Comparison
Here’s the thing: sometimes the most important changes aren't in the HTML source at all. A tweak to a CSS file can transform the layout, a new hero image can alter the entire message, and JavaScript can render dynamic content that a simple HTML check will never see. This is where visual comparison saves the day.
The idea is to take screenshots of the webpage at set intervals and compare them pixel by pixel.
- Benefit: It's the only method that reliably catches rendering changes that checksums and DOM diffs are blind to.
- Drawback: It's the most resource-intensive approach and can be finicky. Minor rendering glitches, font anti-aliasing, or rotating ads can trigger false positives if you're not careful.
A good workaround is to use a screenshot tool that can block ads and pop-ups before capturing the image. This cleans up the comparison process immensely, helping you focus only on the visual changes that actually matter.
To make this choice easier, let's break down how these methods stack up against each other.
Comparison of Webpage Change Detection Methods
| Method | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Checksum (Hashing) | Binary "changed/not changed" alerts on static or API content. | - Incredibly fast and low-cost. - Simple to implement. |
- No context on what changed. - Extremely high rate of false positives from minor/invisible updates. |
| DOM Diffing | Tracking specific content sections, like prices, product availability, or headlines. | - Pinpoints exact content changes. - Can ignore irrelevant page sections, reducing noise. - More efficient than visual comparison. |
- Misses visual-only changes (CSS, images). - Can be tripped up by complex, JavaScript-heavy sites. |
| Visual Comparison | Monitoring for layout, branding, and user interface changes that aren't reflected in the source code. | - Catches all visible changes. - The most comprehensive method for user-facing updates. |
- Computationally expensive. - Sensitive to ads, pop-ups, and minor rendering artifacts without careful configuration. |
Ultimately, the best strategy is the one that gives you the most accurate and actionable alerts for your specific use case. Each method is a tool, and picking the right one is the foundation for building a monitoring system you can actually rely on.
Practical Implementation and Architecture
With your strategy locked in, it's time to get your hands dirty and build the actual monitoring engine. This is where the rubber meets the road. A truly robust system is more than just a script; it’s a well-thought-out architecture that juggles speed, cost, and reliability. The choices you make now will be the difference between a dependable tool and a constant source of late-night maintenance headaches.
First up is the polling cadence—basically, how often you’ll check the page for updates. This decision is critical. Checking a site every five seconds might give you the edge in tracking a flash sale, but it's a surefire way to burn through resources and potentially get your IP address blocked. On the other hand, a daily check is cheap but totally useless for time-sensitive changes. Your goal dictates the frequency.
Headless Browsers vs. API-Driven Services
Once you’ve got a schedule, you need to actually render the target page to analyze it. This is a major stumbling block for many DIY systems. You've got two main paths, and each comes with its own set of trade-offs in terms of complexity and your ability to scale.
Self-Hosted Headless Browsers: Using libraries like Puppeteer or Playwright gives you ultimate control. You can script complex user interactions, manage cookies, and fine-tune every part of the browser environment. But that power comes at a steep price. Suddenly, you're the one responsible for managing browser instances, plugging memory leaks, rotating proxies to avoid getting banned, and scaling the whole setup as you add more pages to monitor. It's a full-time job in itself.
API-Driven Screenshot Services: A service like ScreenshotEngine abstracts away that entire infrastructure nightmare. Instead of wrestling with browser management, you just make a simple API call. The service takes care of the rendering, proxy management, and even blocks common noise like ads and cookie banners for you. This approach dramatically simplifies your code and boosts reliability, freeing you up to focus on the change detection logic.
For most projects, starting with an API is the pragmatic move. It offloads the most frustrating parts of the process, leading to a faster, more stable build. You can always venture down the self-hosted road later if you run into a truly unique requirement that an API can't handle. To get a feel for what’s possible, you can explore the ScreenshotEngine documentation to see all the available parameters and features.
The flowchart below shows how you can layer these different detection methods to create a smart and efficient monitoring pipeline.
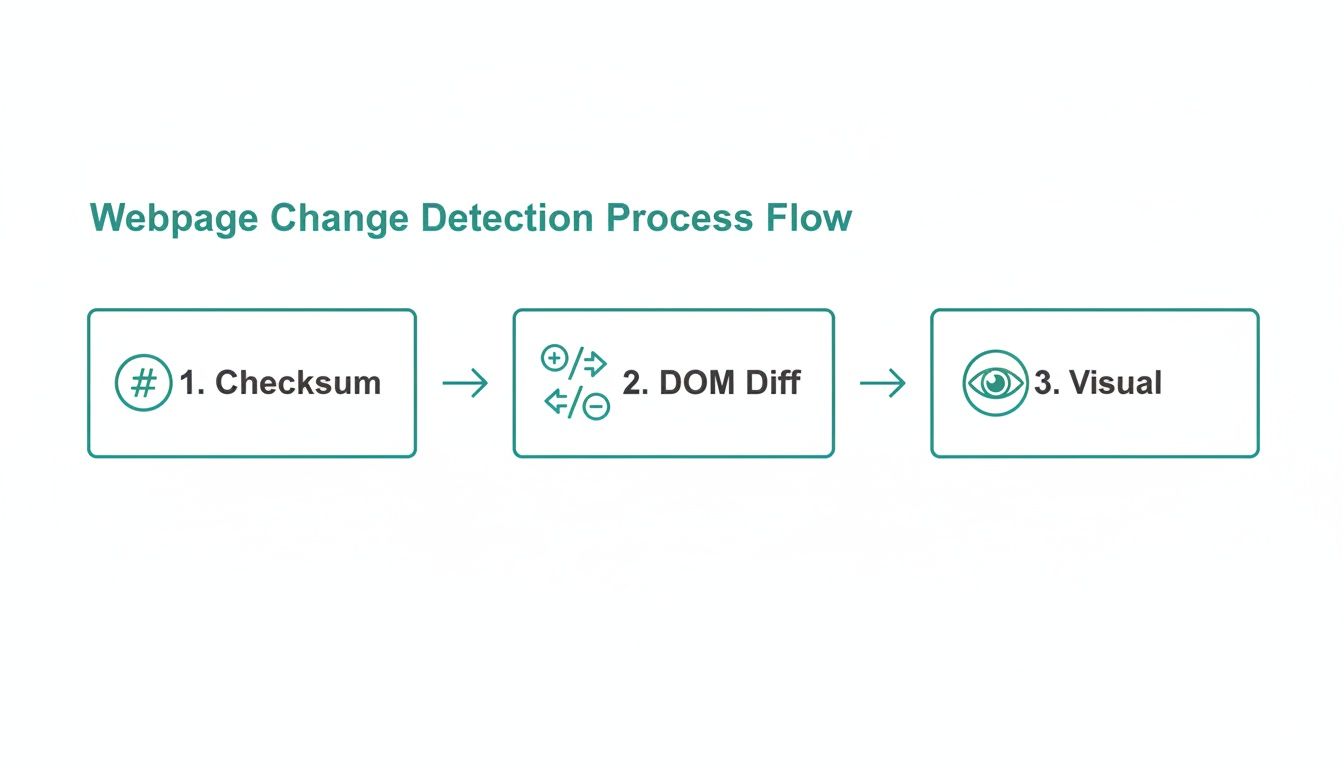
As you can see, you can start with a quick, low-cost checksum and only escalate to more intensive DOM or visual diffs when a change is actually detected.
Designing for Reliability and Scale
A simple script might work just fine for one page, but a production-grade system has to be resilient. What happens if the target site goes down? What if your own network connection fails? Your architecture has to anticipate these real-world hiccups.
This is where a job queueing system (like RabbitMQ or Redis) becomes essential. Instead of running checks directly, you add a "job" to a queue. A separate "worker" process then picks up that job, tries to check the page, and automatically retries if it fails. This decouples scheduling from execution, ensuring that temporary glitches don't cause you to miss an important update.
Building a resilient system means planning for failure. Assume the target website will be slow, network requests will time out, and your IP will get blocked. A queueing system with built-in retries is your best defense against these inevitabilities.
Don't underestimate the business impact of a failing or slow website. Studies have shown that roughly 88% of users will ditch a site that loads too slowly, while fast-loading pages can hit conversion rates approaching ~40%. With over 60% of all web traffic now coming from mobile devices, it's more important than ever to ensure your content is fresh and renders correctly, as slowdowns have an even greater negative effect on user engagement on smaller screens. This reality just reinforces the need for a monitoring architecture that isn't just reliable, but fast.
Alright, theory is one thing, but let's get our hands dirty. It's time to build a real script that actually monitors a webpage for changes using the ScreenshotEngine API. The plan is to go from a simple baseline capture to a fully automated check that sends you an alert when something is different.
We're going to start by grabbing two key pieces of information: a visual screenshot and the page's HTML. This two-pronged approach is essential. It gives us a solid baseline to compare against, letting us check for both visual tweaks and behind-the-scenes content changes.
Nailing the Baseline Capture
Your first API call is the most critical one. This is what sets the "source of truth"—the perfect, clean version of the page that all future checks will be measured against. If you get this wrong, you're just setting yourself up for a flood of false alarms later.
To get a reliable baseline, you have to dial in the API parameters just right.
viewport: Lock this down. Something like1920x1080is a good standard. This forces the page to render the same way every time and stops responsive design from making you think the whole site changed.block_ads: Definitely turn this on. Third-party ads are constantly changing and are the number one cause of visual "noise" that has nothing to do with the actual site content.block_cookie_banners: This one is a lifesaver. It gets rid of those "accept cookies" pop-ups that love to cover up half the page and completely wreck your visual comparison.
Here’s what a clean capture from ScreenshotEngine looks like when you use the right settings.
See? No ads, no pop-ups. Just a stable image that's perfect for accurate change detection.
Setting Up a Recurring Check
Once you've saved that perfect baseline, you'll need a function that runs on a schedule—a simple cron job is perfect for this. This function will hit the API again to grab the page's current state, but here's the key: you must use the exact same parameters as your baseline capture. Consistency is everything. Even a tiny change in the viewport will cause the comparison to fail.
After you get the new screenshot and HTML, it's time to see what, if anything, has changed.
- Content First: The fastest check is to run a checksum (like SHA-256) on the new HTML and compare it to the hash of your baseline HTML. If the hashes match, you're done. The content is identical, and you can usually skip the visual check altogether.
- Visual Next: If the HTML hashes are different, it's time to bring out the visual diff. Using an image comparison library, you can compare the new screenshot to your baseline pixel by pixel. This is where you’ll catch things a DOM check would miss, like CSS changes or content loaded in by JavaScript.
Here's a pro tip from experience: set a tolerance threshold for your visual comparison. A zero-tolerance check is a recipe for frustration, as it will flag minuscule rendering differences from things like font anti-aliasing. Allowing for a tiny bit of pixel deviation—say, 0.1%—makes your monitor much more reliable.
Sending Alerts That Are Actually Useful
When your script detects a real change, the final step is to sound the alarm. Don't just send a vague "Hey, something changed" message. That’s not helpful. A good alert gives you context right away.
Make sure your alerts include:
- A link to the page you're monitoring.
- The exact time the change was detected.
- Both the "before" and "after" screenshots so you can see the difference immediately.
This kind of hands-on approach, powered by a solid API, turns a complicated problem into something you can actually manage and scale. If you want to go even deeper into the technical side of things, check out our complete guide on using a website screenshot API for all sorts of automation jobs.
Managing Alerts and Storing Historical Data
Spotting a change is just the first domino. The real magic is in what happens next—how you get notified and what you can do with that information. If all you get is a generic alert, it’s just more noise in your inbox. To truly monitor webpage for changes in a meaningful way, the final steps of your system have to be just as thoughtful as the detection itself.
The aim isn't just to get notified; it's to get actionable alerts. A vague email that just says "something changed" is a dead end. It forces you to drop everything and manually investigate, which pretty much defeats the whole point of setting up automation in the first place. Good alerts give you context right away.
Designing Alerts That Actually Help
For an alert to be genuinely useful, it has to answer three questions immediately: what changed, where, and when? Anything less is an incomplete story. A solid alert system should also be flexible enough to plug right into the tools your team already uses every day.
Think about where the notifications should go:
- Email: This is a classic for a reason. It’s perfect for low-urgency updates. The key is to embed the "before" and "after" screenshots or text snippets directly in the email body so no one has to go digging.
- Slack or Microsoft Teams: When you need to get multiple eyes on a change quickly, this is the way to go. Pushing alerts to a dedicated channel keeps the conversation focused and everyone in the loop.
- PagerDuty or Opsgenie: For the really critical stuff—like an unannounced change to your terms of service or a price hike on a competitor's site—you need an alert that demands immediate attention.
- Custom Webhooks: This is where things get really powerful. A webhook can kick off a whole chain of events automatically, like creating a new ticket in Jira, updating a row in a database, or even triggering another script.
An effective alert doesn’t just tell you a change happened; it gives you the context needed to decide if you need to act. The difference between a simple notification and actionable intelligence is in the details you provide.
Why You Need to Keep an Archive
Alerts are for the here and now, but storing historical data is your key to unlocking long-term insights. Just checking a page and then throwing away the data is a huge missed opportunity. By building an archive of page captures, you're essentially creating a time machine for a website's evolution.
This historical data can be incredibly valuable. For compliance, it's your verifiable audit trail of any modifications to sensitive documents. For competitive analysis, it lets you track a rival’s pricing changes or messaging shifts over months or even years. If you're curious about the technical side of grabbing these snapshots, our guide on using a screenshot API for automation is a great place to start.
When it comes to actually storing all this data, cloud object storage is the obvious choice. Services like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage are practically built for this. They're cheap, scalable, and make it easy to dump massive amounts of data, whether you're saving full-page screenshots, HTML diffs, or JSON files with metadata. This archive is what elevates your system from a simple alerter into a genuine business intelligence tool.
Common Questions and Roadblocks
When you start building a system to monitor webpages for changes, you'll inevitably hit a few common snags, especially with today's complex sites. Let's walk through some of the most frequent challenges I've seen and how to get past them.
How Do I Deal With Dynamic, JavaScript-Heavy Websites?
You’ll quickly discover that a simple curl or fetch request won't work on modern websites like Single Page Applications (SPAs). The content you actually want to check—the product details, the latest news—is often rendered by JavaScript after the initial HTML has loaded.
The only way around this is to use a tool that can fully render the page in a real browser environment. You could manage your own fleet of headless browsers with something like Puppeteer, or you can offload that complexity to an API like ScreenshotEngine which handles all the rendering for you.
A pro tip: for elements that constantly change on every load, like countdown timers or ad banners, use specific CSS selectors to exclude them from your comparison. This single step will save you from a mountain of false positives.
What’s the Best Way to Avoid Getting Blocked?
Websites are pretty good at spotting and blocking automated scripts. If you want your monitor to run reliably, it needs to blend in and look more like a regular human visitor.
The most powerful technique here is to use a rotating proxy service. This spreads your requests across a huge pool of different IP addresses, making it much harder for a site's security systems to flag you.
Beyond that, always make sure you're doing the basics:
- Set a realistic User-Agent string that mimics a modern browser, like Chrome or Firefox.
- Check and respect the website’s
robots.txtfile—it’s just good practice. - Add a reasonable delay between your checks. Hitting a server every few seconds is a dead giveaway that you're a bot.
A good screenshot API handles proxy rotation and browser fingerprinting for you. Honestly, this is one of the biggest reasons developers opt for a service instead of wrestling with this complex infrastructure themselves.
How Can I Monitor Just One Tiny Part of a Page?
Trying to compare an entire webpage every time is usually overkill. It’s inefficient and often leads to alerts about things you don’t care about, like a new blog post in the footer. If all you need to know is when a price changes or an "out of stock" label appears, then just watch that one specific element.
This is where CSS selectors or XPath expressions become your best friend. After you've rendered the page and have the DOM, use a parsing library to pinpoint and extract only the element you need. By tracking just that element's text or attributes, you create a far more efficient and precise monitor that cuts out all the noise.
Ready to build a rock-solid monitoring system without the headache of managing browsers and proxies? ScreenshotEngine offers a powerful, developer-first API that captures pixel-perfect screenshots of any site. Get started for free and see just how simple it is to automate your change detection workflow.